Brazinskaitė M., Ramanauskaitė A. (2011). The development of long-term relationship between mobile service organizations and consumers. Global Academic Society Journal: Social Science Insight, Vol. 4, No. 12, pp. 26-36. ISSN 2029-0365. [www.ScholarArticles.net]
Authors:
Miglė Brazinskaitė, Kaunas University of Technology, Lithuania
Agnė Ramanauskaitė, Kaunas University of Technology, Lithuania
Abstract
The ability to use and manage properly the advantages of relationship marketing is considered an excellent, exclusive competence of the organization. To develop this competence the organization must understand the essence of the relationship marketing conception. Therefore, this article reveals the concept of relationship marketing, focuses on service consumers – an essential element of the new marketing orientation, and on the formation of long-term relationship with consumers, characteristics, methods and measures that lead to a sustainable, continuous, mutual beneficial interaction. The article analyzes the significance of long-term relationship for the mobile service organizations, the relationship nature of the mobile service users and providers and the main factors affecting that relationship. Lastly, are given suggestions and recommendations for mobile service organizations that strive for consumers’ loyalty.
Introduction
The competitive struggle of the biggest Lithuanian mobile operators promotes a persistent migration of consumers and a growing consumer disloyalty. Therefore, in order to keep consumers, the mobile service providers rely on relationship marketing. Relationship marketing is still a new phenomenon for most Lithuanian companies. The literature on marketing channels has provided numerous definitions of relationship marketing and different authors interpret it differently. Even so authors agree that this phenomenon for every organization is individual and shows the importance of development long-term relationship with consumers.
Object – relations between mobile service providers and consumers.
Purpose is to identify the peculiarities of developing relationship between mobile service organizations and consumers.
Tasks:
- To disclose the importance of long-term relationship with consumers in the mobile service organizations.
- To identify reasons that influence consumers to keep long-term relationship with mobile service organizations.
- To make suggestions for mobile service organizations that want to keep long-term relationship with their consumers.
Methods: analysis of scientific literature, documents analysis of mobile service organizations, questionnaire, data analysis using SPSS.
Conception of relationship marketing
At the end of twentieth century have been made a lot of researches of marketing effectiveness, which showed that the effectiveness of marketing activities are directly related to consumer loyalty. Therefore, internal business processes and resources must be used for creating consumers loyalty (Juščius et al., 2006). Thanks to the researches, attention was focused on the need to build and keep relationship with consumers. Gradually the concept of relationship marketing began to form, claiming that the most important is to maintain long-term relationship with consumers. Scientists and practitioners agree that it is necessary to abandon short-term and exchangeoriented goals and move towards building a lasting, valuable relationship with consumers. However, after almost three decades since the first idea of relationship marketing shown, there’s still a debate on the origin of relationship marketing and there’s still not found a single term to describe this concept. The reason of this is the development of relationship marketing, which is affected by an independent and carried out in different directions researches (Kvedaras, 2009;Žvirelienė and Bučiūnienė, 2008; Juščius et al., 2006; Dovalienė and Virvilaitė, 2003). The author of the idea and the term of relationship marketing is an American scientist Berry. In 1983 he presented the first concept of relationship marketing. Berry analyzed the relationship marketing as an instrument of consumer attraction and retention (Fernandes and Proenca, 2005). According to Kvedaras (2009), the first definitions of various authors emphasized the importance of the permanent relationship with the consumer only, while the most recent – the need to establish and maintain long-term relationship with a various subjects affecting the organization’s activities. In conclusion it may be noted that relationship marketing – it’s a system of measures to keep consumers, involving methods and market participants that affect relations between companies and consumers. In the scientific literature are usually discussed five groups models of relations, involving from 6 to 30 different participants, identified by the authors such as Juščius et al. (2006), Hopenienė and Minkštimienė (2002) and others. However, the development of relationship marketing that began from the idea that the most important for companies is to create long-term relationship with consumer, allowing to exclude a group of consumer over other groups of relationship. The creation of long-term relationship with consumer is probably the one of the most significant thing which has a very positive impact on business future. However, the persistent mobile service consumers’ migration highlights the importance of the formation and development of long-term relationship and the importance of these processes for mobile service organizations. So for carrying out further investigations primarily need to examine the relationship with consumers market, which takes a key role in marketing.
The formation of long-term relationship with consumers
Analyzing the relationship marketing it is very important to understand which features long-term relationship has. Various authors, such as Buttle, Kėdaitienė, Gummesson and others, state that long-term relationship involve such features as trust, power, meeting the needs, durability, mutual dependence, risk, profit, promises to respect, commitment, communication, cooperation and so on (Bagdonienė and Hopenienė, 2005). However, many authors consider trust and commitment as the main principles of maintaining long-term relationship with consumer. It should be noted that in order to develop long-term relationship, trust and commitment must be mutual. As Ryssel et al. (2004) claimed, consumer trust is the level to which consumer believes that the supplier is honest, benevolent and competent. Meanwhile, consumer commitment is defined as his/her strong desire to develop and maintain long-term relationship with the provider. This is based on the belief that the relations, their maintenance is well worth the effort. According to Ulaga and Eggert (2004) analysis, satisfaction and commitment have a direct impact on consumer behaviour. Satisfaction and commitment increase desire to expand relations with existing service provider and reduce the propensity to leave the provider. Long-term relationship with consumers is created by developing their loyalty to the company.
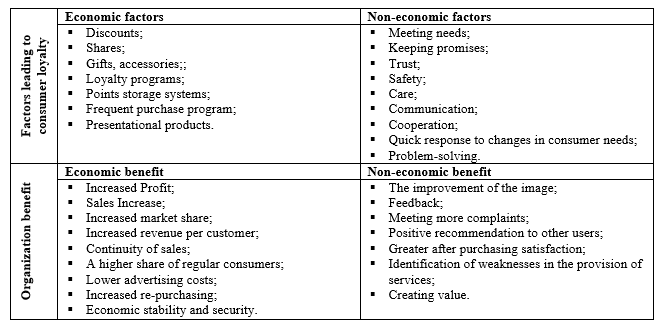 Table 1. The benefit of long-term relationship (made by the authors according to Pajuodis, 2005; Bagdonienė and Hopenienė, 2005; and others)
Table 1. The benefit of long-term relationship (made by the authors according to Pajuodis, 2005; Bagdonienė and Hopenienė, 2005; and others)
Different authors interpret loyalty differently. Dainauskaitė (2009) states that all definitions of loyalty are distinguished by two elements: faithfulness and devotion. In addition, nowadays is growing concerns about the importance of attachment to the trade mark of loyalty. Modern marketing experts point out that loyalty is not possible without real attachment, because the market of these days is full of companies that deal with the same or very similar products. The companies that want to maintain their positions, to find new consumers and expand do an active policy of loyalty. According to Dainauskaitė (2009), consumer loyalty is the most important aim of relationship marketing because loyal consumers have the direct impact on companies’ efficiency. Customer loyalty is related to profitability, based on the following facts as lower marketing costs for the maintenance of loyal consumers, the opportunity to sell related products and setting a higher price for the product or service. The consumer becomes loyal gradually moving on particular stages. Bakanauskas and Pilelienė (2008) distinguish four stages of customer loyalty: cognitive loyalty, an emotional loyalty, a simple loyalty and action loyalty. Identification of loyalty stages and meeting the consumer needs give organization a competitive advantage. However, to maintain consumer loyalty is not so simple – it is a long-term process that requires continual organization’s efforts. Since consumers do not always tend to remain loyal to the organization, in order to keep them, organizations take specific measures (see Table 1). It can be stated that long-term relationship – the equivalent exchange, involving mutual benefit, i.e., get benefit not only organizations but consumers also. Long-term relationship that is focused into a permanent interaction with the customer, give organizations not only economic stability, but at the same time the non-economic benefit such as positive recommendations to other consumers, improvement of the image, more feedback and so on. Long-term relationship is developed through mutual trust, and then consumers feel safe and happy. However, it should be noted that in order to maintain and strengthening long-term relationship is very important to provide the maximum satisfaction for every consumer that it would be difficult for competitors to attract them offering lower prices or in other ways.
Methodology
For selection of respondents convenient sample were used when interviewing that consumers which are easy to find. Doing the selection of respondents were used no systematic mechanism, just was selected conveniently reached 18 years of age and older people who use mobile services. Questionnaire was posted on the website and link to the questionnaire were sent to the e-mail and placed in the social pages with the request that it be filled. 200 respondents participated in the study – 146 women and 54 men, aged between 18 and 60 years. The questionnaire contains 20 questions. This is an anonymous questionnaire so the respondents’ identification is not required. The questionnaire consists of two open-ended questions and 18 closed. Answering to closed-ended questions, 11 – out of them respondents have to choose one, and 4-s – more suited to their answers. The questionnaire has one the rating scale, a response matrix and the hierarchy form question. The first 14 questions are for evaluating consumer satisfaction with services and to investigate the cause, encouraging mobile users to stay in the organization or to change mobile service provider. Meanwhile, 6 other remaining questions are for respondents’ gender, age, education, employment and monthly income determination. The survey data are summarized in Microsoft Excel and data were processed and analyzed using SPSS program, which led to the valid conclusions assessing survey questions answers according to certain features of groups or differences.
Research results
In order to identify the mobile service provider’s efforts in creating and developing longterm relationship with consumers was conducted documents analysis of mobile service organizations. Three the largest Lithuanian companies, i.e. “Tele2”, “Omnitel” and “Bitė Lietuva” were compared by the measures that mobile organizations use to retain their consumers. These measures are divided into four groups: the range of services, service quality, pricing and promotion. The analysis has revealed that “Tele2” for maintaining and attracting new consumers uses low prices, offering only basic mobile services and various actions for mobile phones and plans with long-term contracts. Also this operator is distinguished by its non-traditional advertising. Meanwhile, “Bitė Lietuva” keeps a balance between price and quality, reach for customer loyalty through promotions and various actions. “Omnitel” stands a better quality of mobile connection, wider range of services which involve the latest generation technology and the loyalty program for stable consumers. “Tele2”, “Bitė Lietuva” and “Omnitel” contributes to a variety of events and projects for encourage the public welfare. To that company want to strengthen its image and to bring greater consumer confidence. Meanwhile, the investigation of customer relationship with mobile service providers revealed that the respondents are loyal to their mobile service organizations. This is evidenced by the long use of the same operator, satisfaction and a high respondents’ level of trust and their willingness to recommend the using operator to other consumers. In order to assess the consumer and mobile service providers in the long-term relationship were evaluated the respondents’ duration of using particular operator. According to the survey it was found that the largest share (39.1%) of respondents use particular operator for 7-10 years, 4-6 years the selected operator’s services are used by 31.5% of respondents. These two longstanding mobile service providers customer group consists of about ¾ of the respondents. The analysis of the respondents’ level of trust (see Figure 1) reported a high average grade (3.48 points out of possible 4). So it can be said that consumers are tend to create long-term relationship with mobile service providers. Respondents, who use “Bitė Lietuva” services, have the highest level of trust on that operator.
 Figure 1. Consumers’ trust on the operator
Figure 1. Consumers’ trust on the operator
Satisfaction has a direct impact on customer loyalty and development of long lasting relationship. The results showed that the 56.9% of respondents are satisfied with providing operators’ services. High level of satisfaction with the services has about 60% of “Tele2” users. Meanwhile, 26.5% of “Bitė” users have the highest level of satisfaction. Respondents’ loyalty to “Bitė” confirms willingness to recommend this mobile service provider to other consumers. Overall results showed that 71% of mobile service consumers would recommend the selected operators to others. The company “Bitė Lietuva” would be recommended by 82.4% of respondents, “Tele2” – by 75.9% and “Omnitel” – by 52.9% of respondents (see Figure 2). It is worth noting that respondents, who use “Omnitel” services, comparing with “Tele2” and “Bitė Lietuva” previously described three criteria, valued the worst. To determine how respondents assess their own dedication to service providers, the survey respondents have evaluated their loyalty in the five-point system. The obtained results showed that the mobile service users participated in the survey are the most loyal to the company “Tele2”. The study also found that consumers are maintaining long-term relationship with mobile service organizations the most for economic factors, i.e. the price and discounts, actions for payment plans. These results suggest that respondents providing a priority for economic factors have a cognitive loyalty. This means that respondents loyalty depends on the costs and benefits ofthe proposal and is not associated with the product brand. Such consumer loyalty is the weakest, so for operators are not useful, because any increase in prices of certain operator or a competitor offering lower prices, consumers do not hesitate to replace long-used operator. That is revealed in the investigation and by the factors driving change the operator. According to respondents, the focus of such a decision would lower prices, better terms of payment plan and family members going to another mobile service provider.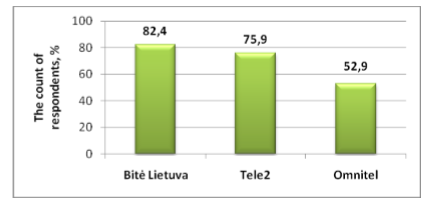 Figure 2. Consumers’ recommendations about the mobile operator
Figure 2. Consumers’ recommendations about the mobile operator
In the summary of these results, it can be said that between the respondents and mobile service providers there are long-term relationship. Features, which are the most typical to describe relationship between service provider and consumer, are keeping promises, satisfaction and safety. The investigation of mobile service organizations allows the measures to evaluate operators use for customer satisfaction and creation of long-term relationship. The study found that the company “Tele2” using smallest price strategy is truly effective. The results showed that the highest loyalty to the operator has respondents using “Tele2” and the main factors for “Tele2” consumers’ loyalty to the company are actions and discounts for payment plans. “Tele2” pricing policies have a significant impact on mobile service consumer choice, satisfaction and willingness to stay with the same organization. The half of “Omnitel” consumers participated in the research use that operator services because of good connection quality. Also respondents’ loyalty to “Omnitel” services reveals consumer possibility to the discount program in other companies that provide the loyalty card “OmniID”. It is obvious that “Omnitel” users are well aware of this service provider’s benefits and strengths of its sides. However, the lowest score among the three major operators in Lithuania evaluated consumer satisfaction with services, relationship characteristics, trust and loyalty, show that using these measures of consumer retention is not enough. “Bitė Lietuva”, which discovered a compromise between price and quality of service, deserved a particularly high level of consumer confidence and satisfaction with services and quality of relationship development. Among all “Bitė Lietuva” consumers, participated in the study, was no one respondent who is not satisfied with services of this operator. In addition, a third part of respondents using “Bitė Lietuva” did not know the reasons that could lead them to change this mobile service provider. So, it can be said that used measures by “Bitė Lietuva” for consumer retention, satisfaction and loyalty development are effective.
Suggestions and recommendations in order to maintain long-term relationship with consumers
The study showed that costs and benefits of proposals have the greatest impact on the choice of operator. It can be concluded that the respondents’ loyalty for mobile service providers is cognitive. According to Bakanauskas and Pilelienė (2008), defined stages of consumer loyalty, cognitive loyalty is considered the weakest, because users tend to change service provider when get a proposal of better cost-benefit ratio. This is also proved by the market share changes of the largest Lithuanian operators. Therefore, in order to maintain stronger relationship with the clients, mobile service providers should seek the higher stage of consumer loyalty in an effort to promote customer loyalty not just economic measures, such as low prices or discounts, but proving their honesty to the consumer, providing a sense of security, caring for him/her and always keeping the promises made. Study found that a false suggestions and breach of contract cause respondents’ dissatisfaction with the services provided. This kind of dissatisfaction with the service of selected operator could be reduced by providers’ honesty and openness. In other words, before signing a long-term contract, mobile service providers should provide to consumers full in-depth information not hiding additional conditions that consumer does not know. A few years ago Lithuanian operators widely used small „stars“ and text in very small writing betrayed a payment conditions that was not the best for consumer. Such actions and methods had a negative impact on value of the mobile service providers. Therefore, in order to maintain long-term relationship with consumers, openness is essential. A study has identified and another cause of consumers dissatisfaction with the services. It’s a lack of mobile operator’s efforts to solve consumers’ problems. However, this situation is quite difficult to assess because there are no known scale of the problems, reaction time and the action taken. It should be noted that operators have founded rapid response units, available in the visit, by telephone or the internet, posted the most topical problem-solving techniques on the internet and make it possible to find a solution of the problem. Therefore, the only method offered shall be to raise consumer awareness about the potential solution to the problems not only in making calls or communicating directly with employees but also contacting in specially designated areas where users can ask questions, complain and get professional response. Furthermore, consumers make a mistake, looking for help only at the last minute. It is worth to encourage consumers to contact emergency that the information reaches the participants of relations in time. Each company aims to attract more new consumers for the principal purpose – to increase revenue and profit. However, operators, with a clear focus on new consumers, abandon the current. In order to maintain long-term relationship with consumers is extremely important to show consumers their value for the organization. This function can perform various loyalty programs for loyal consumers, exclusive offers and extra discounts for a certain amount of account or service rates, depending on the duration of use of services. Thus expressed gratitude for many years of cooperation enhances consumer satisfaction and the desire to remain organization’s customer. Furthermore, creating measures to develop loyalty of existing consumers, it’s very important to present them, introduce and if it’s necessary, remind consumers of their existence and purpose. On the other hand, the largest efforts of mobile service providers to maintain long-term relationship with consumers can be meaningless, if consumers perceive different content and significance of relationships, aims to one-sided advantage. Long-term relationship is a long process that requires sustained effort by both participants.
Conclusions
- The competitive struggle of the largest Lithuanian mobile operators promotes a persistent migration of consumers, therefore in today’s market a company’s long winning intention is consumer maintenance. Long-term relationship, that are focused on continuous interaction with the consumer, brings not only economic stability and security, but at the same time non-economic benefits such as positive recommendations to other users, improvement of the image, the identification of weaknesses in the provision of services and many others advantages. Furthermore, thanks to long-term relationship, is reached larger and long-term outcome with low financial cost.
- The study of consumers and mobile service providers’ relationship showed that a longterm relationship between mobile service organizations and its consumers exist. Loyalty is driven mainly by economic factors, such as price and service discounts, promotions for a payment.
- Evaluated the characteristics of developing relationship between mobile service organizations and its consumers, for operators, who seek to maintain long-term relationship with consumers, are suggested: to achieve higher consumer loyalty stage, communication and the proposals based on openness, stimulate consumer participation and improve problem-solving techniques, demonstrate consumer awareness of ways to solve problems, and to show and remind consumers about the importance of them for organization.
References
- Bagdonienė L., Hopenienė R. (2005). Paslaugų marketingas ir vadyba. Kaunas. pp. 421-450.
- Bakanauskas A., Pilelienė L. (2008). Vartotojų lojalumo stadijų nustatymo modelis. Available at: http://www.minfolit.lt/arch/16501/16577.pdf
- Dainauskaitė R. (2009). Komercinių bankų klientų lojalumo formavimo modelis. Available at: http://vddb.library.lt/fedora/get/LT-eLABa-0001:E.02~2009~D_20090626_094740-09551/DS.005.0.02.ETD
- Dovalienė A., Virvilaitė R. (2003). Santykių marketingo konceptualioji esmė ir ištakos. Inžinerinė ekonomika. Nr. 2 (33), pp. 100-105.
- Fernandes T. M., Proenca J. F. (2005). Relationships and Relationship Marketing: An Interdisciplinary Perspective. Available at: http://www.impgroup.org/uploads/papers/4686.pdf.
- Hopenienė R., Minkštimienė A. (2002). Ryšių marketingo paradigma: suvokimo erdvė. Ekonomika ir vadyba. Nr. 1 (6), p. 69-76.
- Juščius V., Navickas V., Jonikas D. (2006). Santykių marketingas: teoriniai aspektai. Verslas: teorija ir praktika, t. 7, Nr. 4, pp. 254-253.
- Kvedaras M. (2009). Santykių rinkodaros koncepcijos ir esmės teorinis pagrindimas. Mūsų socialinis kapitalas – žinios: 9-osios studentų mokslinės konferencijos pranešimų medžiaga, pp. 138-144.
- Pajuodis A. (2005). Prekybos marketingas. Vilnius. pp. 273.
- Ryssel R., Ritter Th., Gemunden H. G. (2004). The Impact of Information Technology Deployment on Trust, Commitment and Value Creation in Business Relationships. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing. Vol. 19, No. 3, 2004, pp. 197-207.
- Ulaga W., Eggert A. (2004). Relationship Value and Relationship Quality. European Journal of Marketing. Vol. 40, No. 3/4, 2006, pp. 311-327.
- Žvirelienė R., Bučiūnienė I. (2008). Santykių marketingo dimensijų vaidmuo išlaikant vartotojus. Verslas: teorija ir praktika. T. 9, Nr. 4 , pp. 272-280.
